For retailers, inventory planning matters. Inventory is your largest asset and has the greatest impact on your business cash flow. If you plan your inventory well, you can reduce your overhead costs and increase cashflow. This article will help you understand the essentials to inventory management for retailers.

Cashflow sitting in old or out-of-season inventory is money that could be better used elsewhere. Many successful retailers don’t carry a lot of excess stock to have the flexibility to introduce new products more quickly. This is particularly true in industries such as grocery where products can easily expire or fashion where products can be trendy. All products are worth less over time as they get “stale.” But in fast-moving sectors, products have shorter life cycles, meaning they lose their value faster. As such, carrying too much stock means an increased chance of getting stuck with products that require deep discounting to free up your cashflow. Consider this the next time your suppliers offer you better prices to buy a larger volume of product.
Remember though, keeping your inventory “lean” doesn’t only mean keeping stock levels low. If stock levels don’t match your sales demand and are kept too low, you will constantly have out-of-stock products. You want to avoid stock-outs as they are costly to retailers. They lead to lost sales, wasted marketing efforts, and unhappier customers.
There are many different inventory management methods but ultimately, it comes down to one thing, “do you have stock when you need to sell it“.
In the end, selling at any price is not the objective. To be profitable, retailers need loyal, repeat customers that don’t require expensive marketing campaigns to get them to buy. When you think of it this way, inventory is an important part of your overall customer service. Customer service is the new marketing as every touch point impacts how your customers view your business. Less stock-outs means higher sales in-store and faster fulfillment for online orders, all of which means better customer satisfaction.
What Can I Do As A Retailer To Better Manage My Inventory?
If you’re a small-to-midsize retailer and all of this sounds scary, don’t worry. Not all retailers have the resources of the big brands, and regardless of your size, there are things you can do to better plan your inventory.

1) Make Sure You Always Have Access To Real-Time Stock Levels
You can’t manage what you don’t know. With an increasing number of sales channels (e.g. e-commerce, pop-ups, etc.), a retail POS that can handle “unified commerce” with real-time stock levels is essential to inventory management in today’s market. Unified commerce is just another way of saying a total retail management platform that you can log into from anywhere that offers a single view of inventory, sales, and customer data across an entire business in real time. As expected, the need for real-time inventory data grows as the business and transaction complexity increases.

2) Use Minimum Stock Levels
Use minimum stock levels, also known as safety stock levels. In many retail point-of-sale systems, you can assign a minimum stock level to every product in your store which you can easily track in comparison to your actual stock level. You should also be able to easily make mass updates in your POS when you review your minimum stock levels every 3-6 months.
3) Track Inventory Stock Levels By Supplier
Track inventory stock levels by supplier so that you can consolidate purchases to minimize stock-outs, lead time, and shipping costs. This will also allow you to more easily meet supplier minimum order amounts.
4) Track Inventory Turnover
This is essential to inventory management in retail. Basically this refers to how many times a product is sold and replaced over a certain period of time. This can be tracked at a very high level (e.g. including the entire store inventory) or at the product / category level. There are different ways to calculate turnover but whatever approach you use, consider using Cost of Goods Sold instead of Sales as you will get a more accurate measure as your result will not include markup. For example:
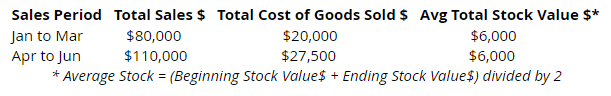
- From Jan-Mar, this company had inventory turnover of 13.33. This is calculated by taking the Sales$ for this period and dividing it by Average Stock Value$. Now you can convert this to “inventory days” by taking 365 / 13.33. So from Jan-Mar, inventory turns 13.33 times a year and is on hand for approximately 27.38 days. If you run the same calculations for Apr-Jun, inventory turns 18.33 times a year and is on hand for approximately 19.91 days.
- From these two examples, the higher your turnover rate, the more efficient you are, since it means that your inventory is being sold faster and you have more cash flow in your business. A lot of people forget that the cost of inventory is not just the original purchase cost of an item. It includes the ongoing cost TO SELL that inventory. The longer it takes to sell something, the greater your real inventory cost as your money is sitting in that dead stock instead of products that are in high demand.
5) Determine Your Ideal Reorder Days
It is always a good idea to estimate the lead time required to reorder products in time for suppliers to produce OR deliver them before you are out-of-stock. For example, if you know it takes two weeks to receive orders from a particular vendor, make sure to factor that lead time into your reorder timing. In the beginning, you don’t want to cut it too close as unexpected delays can happen (e.g. snowstorms in the winter). This is especially true if you are ordering for a busy time of year such as Christmas. For some retailers, losing a week during the holidays might mean the difference between Christmas and Boxing Day pricing.

Inventory Management – Essential For All
A lot of independent retailers or businesses often think that they are not large enough to use inventory management tools and try to use spreadsheets to keep track of their goods. While this can work in the beginning, as your inventory items grow in both size and attributes, you will either overstock (to prevent stock-outs) or have constant back orders. You will also lose out on freight savings and volume discounts you might have received if you had consolidated your vendor orders more efficiently.
Start improving your operations by following the key essentials to inventory management we’ve listed above. Then when you’re ready, start to slowly automate these functions one-by-one. With the proper point-of-sale system, you will be able to spend less time managing your inventory and more time selling it.
We hope you found this article helpful! Subscribe to our blog for more helpful retail tips and strategies!

This article is an updated version of a blog post first published in the ACE POS Solutions blog.


